Working Time
-
Mid-week 09:00 - 21:00
Saturday 09:00 - 21:00
Sunday: Close
Contact Info
-
0212 651 42 42
- [email protected]
Ask Question
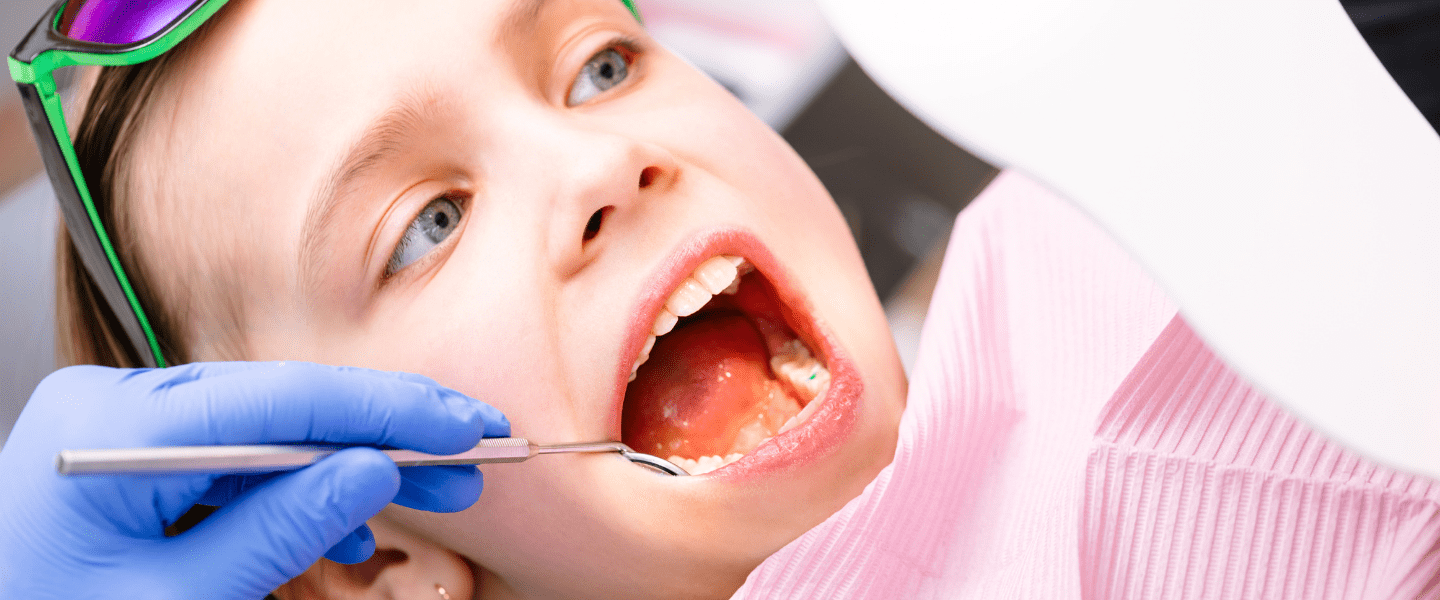
Periodontology
Periodontology is a branch of dentistry that examines the health of the soft and hard tissues surrounding the teeth and aims to diagnose and treat diseases related to these tissues. Teeth are not directly attached to the jawbone; they are located in the alveolar ridges within the jawbone. Inside these protrusions, there is a fibrous connective tissue called “periodontal ligament” between the tooth root surface and the jawbone. This ligament absorbs the forces coming to the teeth and transmits them smoothly to the jawbone. The gums and oral mucosa cover and protect these structures and therefore all these structures are called “periodontal tissues”.
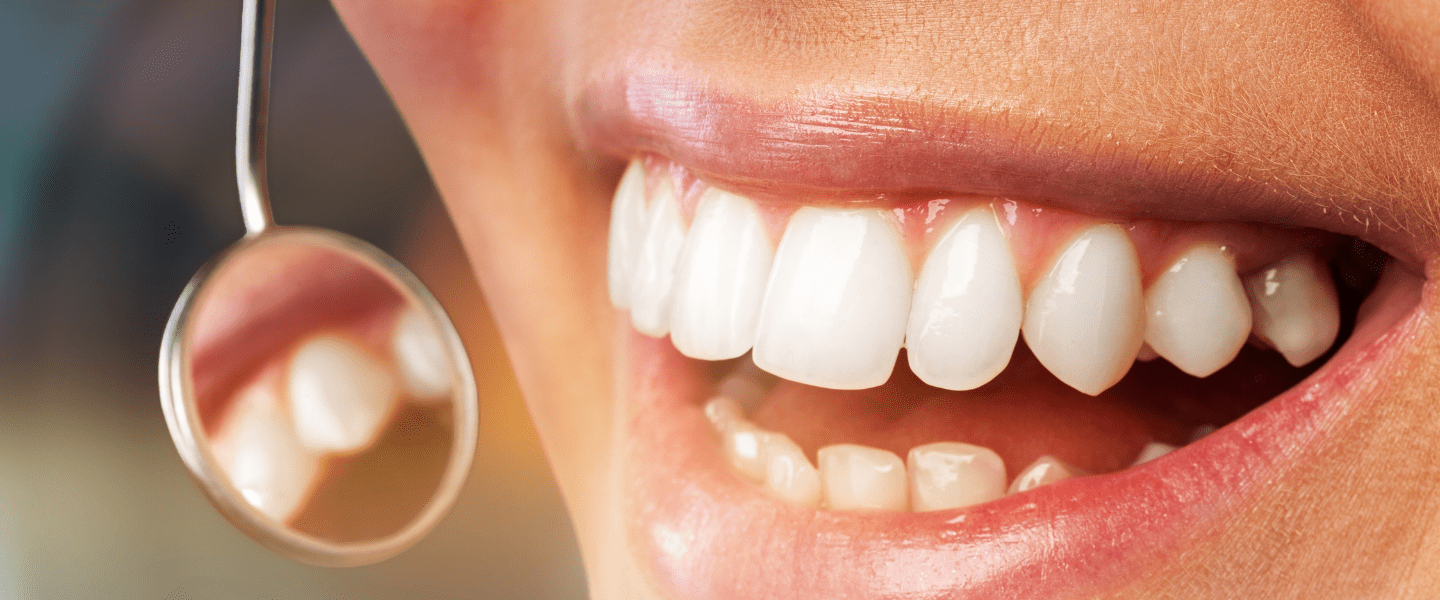
Characteristics of Healthy Gums
A healthy gum is light pink in color, matte in appearance and slightly rough on the surface. The gum wraps tightly around the tooth and forms a thin, sharp border where it meets the tooth. No bleeding occurs during brushing and no pain or discomfort is felt in the gums.
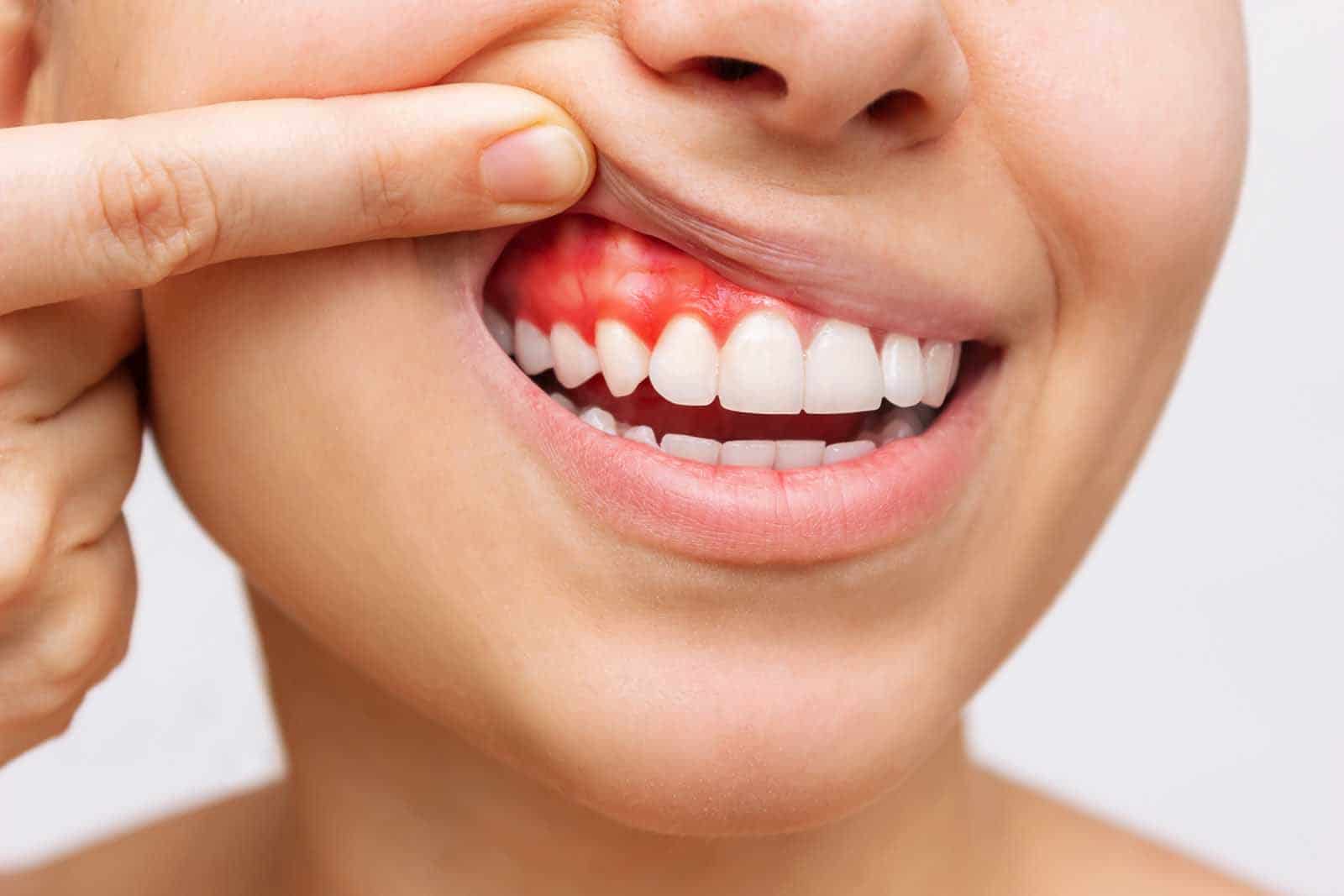
Periodontal Diseases and Gingival Problems
Periodontal tissues can become inflamed due to the bacterial layer known as “microbial dental plaque” that accumulates on the surfaces of the teeth. This inflammation can progress without initially showing obvious symptoms and can therefore be difficult to recognize. Untreated gum disease can lead to tooth loss. In the first stage, the inflammation is limited to the gums and is called “gingivitis”. However, when the inflammation progresses and spreads to the periodontal ligament and alveolar bone, a more serious condition called “periodontitis” develops. At this stage, teeth can become loose and tooth loss can occur.
What is Tartar?
Tartar is calcified and hardened deposits as a result of insufficient cleaning of microbial dental plaque. Tartar creates a favorable ground for new plaque to adhere due to its rough surface. Once formed, tartar cannot be removed with daily oral care at home and requires a professional dental cleaning.
What is Gingivitis?
Gingivitis simply refers to inflammation of the gums, which if left untreated can lead to more serious periodontal disease. In this case, the gum becomes red, swollen and shiny. Bleeding during brushing is a common symptom. When detected at an early stage, maintaining hygiene may be sufficient to control and treat the disease.
What is Periodontitis?
Periodontitis occurs when gingivitis spreads beyond the gum tissue to the periodontal ligament and alveolar bone. This can lead to the formation of pockets around the teeth and bone loss. As periodontitis progresses, teeth may become loose, the distance between them may increase and tooth loss may become inevitable. Treatment usually requires surgical intervention, during which procedures are performed to compensate for the loss of soft and hard tissues.
Symptoms of Gum Diseases
Symptoms of gum disease include bleeding gums, changes in the color and shape of the gums, persistent bad breath, swollen and sensitive gums, loose and loose teeth.
Causes of Gum Diseases
The most common cause of gum disease is the sticky layer called “bacterial plaque” that accumulates on the tooth surface. However, factors such as genetic predisposition, smoking, hormonal changes, stress, poor diet, diabetes can also negatively affect gum health.
Prevention of Gum Diseases
The most effective way to prevent gum diseases is to perform daily oral care regularly and correctly. Regular brushing and flossing are essential to prevent plaque build-up. In addition, regular dental check-ups are important for early diagnosis and treatment of diseases. In this way, it is possible to maintain gum health and avoid periodontal diseases.
STUDENT ORAL AND DENTAL HEALTH
Online